
Land can rise through processes such as sediment accumulation (the process that built the Mississippi River delta) and geological uplift (for example, as glaciers melt and the land below is no longer weighed down by heavy ice). The sea level changes that affect coastal systems involve more than just expanding oceans, however, because the Earth’s continents can also rise and fall relative to the oceans. Higher sea level also makes coastal infrastructure more vulnerable to damage from storms. Rising sea level inundates low-lying wetlands and dry land, erodes shorelines, contributes to coastal flooding, and increases the flow of salt water into estuaries and nearby groundwater aquifers. As water warms, it expands slightly-an effect that is cumulative over the entire depth of the oceans (see the Ocean Heat indicator).Ĭhanging sea levels can affect human activities in coastal areas.Changes in the volume of water and ice on land (namely glaciers and ice sheets) can increase or decrease the volume of water in the ocean (see the Glaciers indicator).Temperature and sea level are linked for two main reasons: 3 Relative sea level also has not risen uniformly because of regional and local changes in land movement and long-term changes in coastal circulation patterns.Īs the temperature of the Earth changes, so does sea level. While absolute sea level has increased steadily overall, particularly in recent decades, regional trends vary, and absolute sea level has decreased in some places.At those sites, even though absolute sea level has risen, land elevation has risen more rapidly. Meanwhile, relative sea level fell at some locations in Alaska and the Pacific Northwest.
coastline between 19, particularly the Mid-Atlantic coast and parts of the Gulf coast, where some stations registered increases of more than 8 inches (see Figure 2).


These items are displayed at the time they were affecting sea level. Items with pluses (+) are factors that cause global sea level to increase, while minuses (-) are what cause sea level to decrease. The second graph, which is from coastal tide gauge and satellite data, shows how much sea level changed from about 1900 to 2018. The first graph tracks the change in global sea level since 1993, as observed by satellites. Sea level rise is caused primarily by two factors related to global warming: the added water from melting ice sheets and glaciers, and the expansion of seawater as it warms.

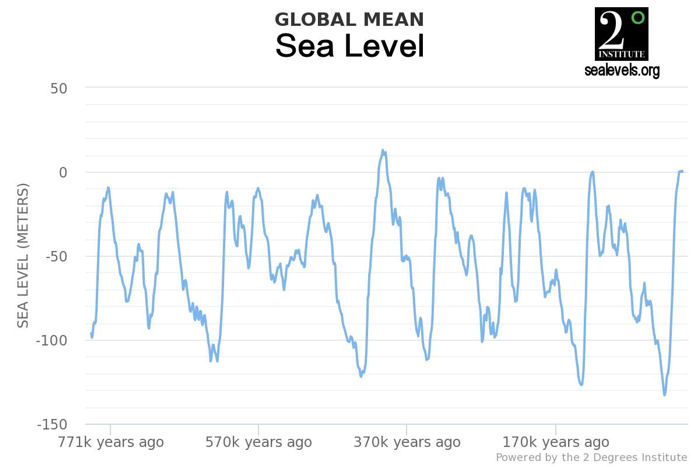
Global sea levels are rising as a result of human-caused global warming, with recent rates being unprecedented over the past 2,500-plus years.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
